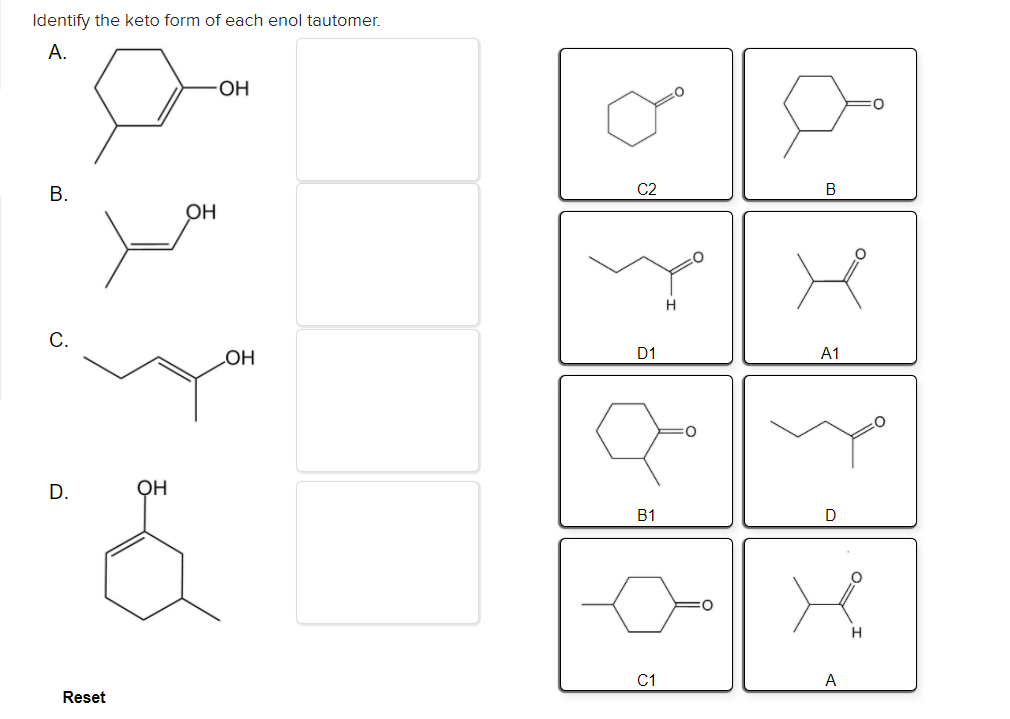
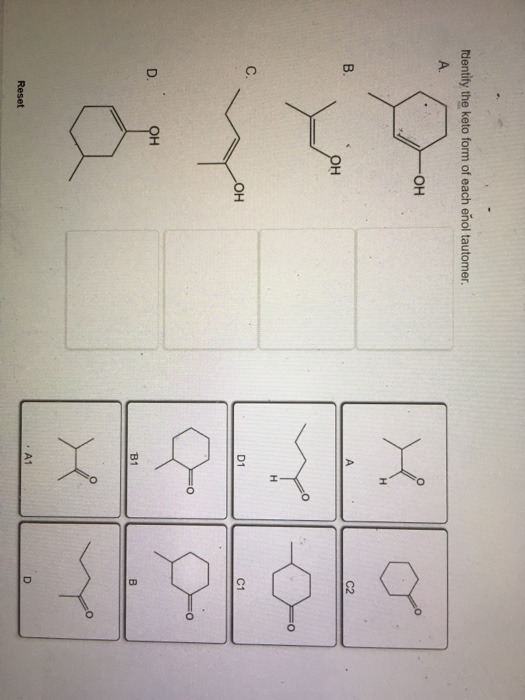
Identify The Keto Form Of Each Enol Tautomer
Identify The Keto Form Of Each Enol Tautomer - Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure and properties of this “enol” form, go through the mechanism for the keto. Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or can form a. Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called.
SOLVED Draw the keto form of each enol tautomer.
Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure and properties of this “enol” form, go through the mechanism for the keto. Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or.
Solved YouTube Identify the enol form of each keto tautomer
Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or can form a. Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure and properties of this “enol” form, go through the mechanism.
Solved Identify the keto form of each enol tautomer. А. ОН
Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or can form a. Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure and properties of this “enol” form, go through the mechanism.
KetoEnol Tautomerism Key Points Master Organic Chemistry
Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or can form a. Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure.
[Solved] Please help . Identify the keto form of each enol tautomer. A. OH... Course Hero
Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure and properties of this “enol” form, go through the mechanism for the keto. Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called. Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Web in the.
Solved dentify the keto form of each enol tautomer он C2 C.
Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called. Web in this article we’ll explore the structure and properties of this “enol” form, go through the mechanism for the keto. Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert.
Solved Problem 11.11 Draw the keto tautomer of each enol. a.
Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called. Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or can form a..
[Solved] Please help . Identify the keto form of each enol tautomer. A. OH... Course Hero
Web in the presence of a proton source, the product can either revert back into the starting ketone or aldehyde or can form a. Web the individual keto and enol isomers are called tautomers. Note the difference between tautomers and resonance forms. Web this spontaneous interconversion between two isomers, usually with the change in position of a hydrogen, is called..
Identify the enol form of each keto tautomer