What Kinds Of Elements Form Covalent Bonds
What Kinds Of Elements Form Covalent Bonds - Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. The number of bonds an element forms in. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. Web a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
Web a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. Web a.
Introducing Covalent Bonding Montessori Muddle
Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when..
How is a covalent bond formed
In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. The number of bonds an element forms in. Web a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that.
Chemical Bonds · Anatomy and Physiology
Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. The number of bonds an element forms in. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar.
Examples of Covalent Bonds and Compounds
Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. The number of bonds an element forms.
Covalent bonding tecscience
Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. The number of bonds an element forms in. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage.
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds.
Covalent Bond Definition, Types, and Examples
In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Web a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons..
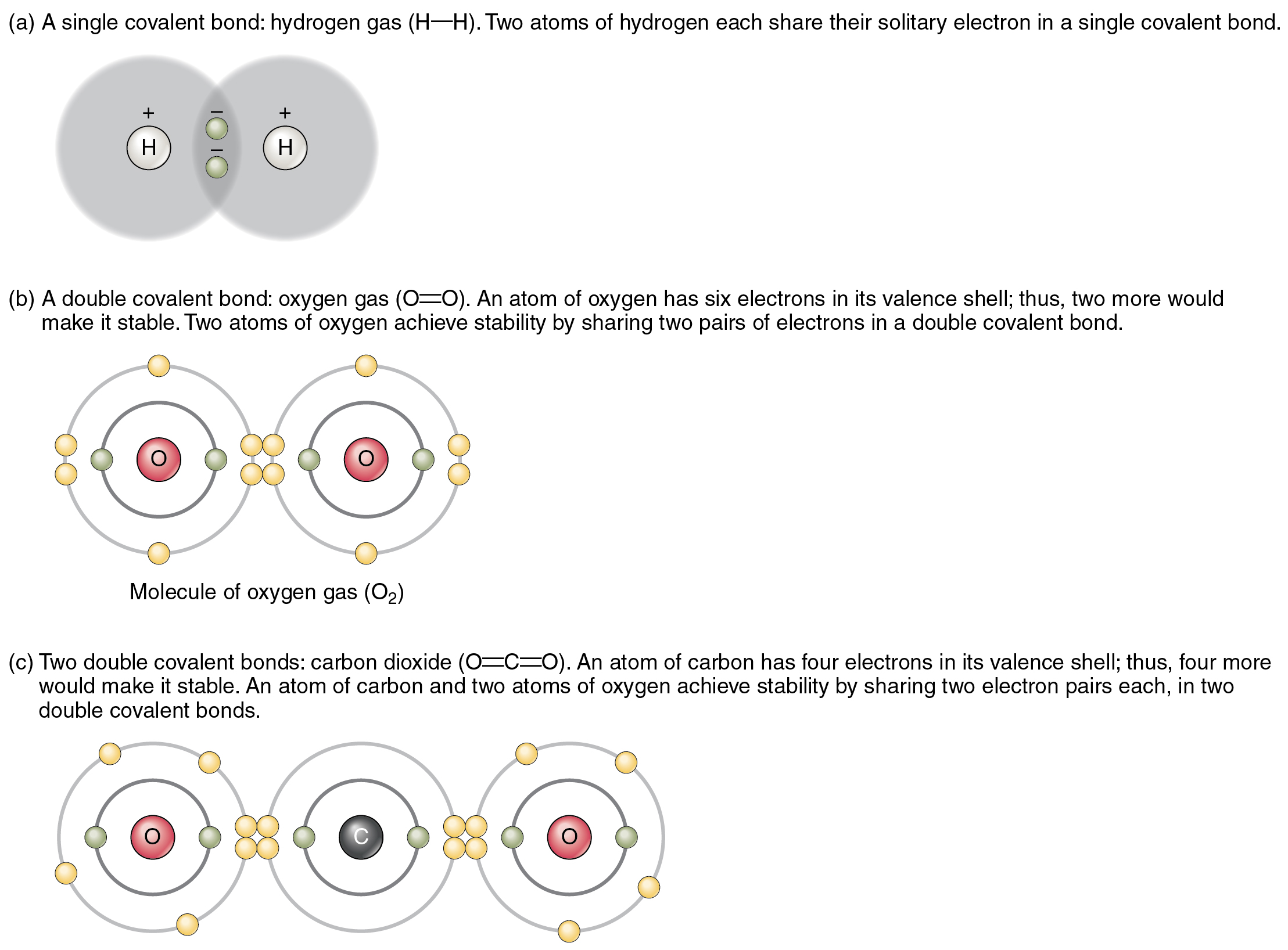
Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. The number of bonds an element forms in. Web a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when. Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms.
Web A Covalent Bond Is Formed Between Two Atoms By Sharing Electrons.
Web a covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. Web a covalent bond is a type of chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. The number of bonds an element forms in.
Web Covalent Bonds Are Formed Between Two Atoms When Both Have Similar Tendencies To Attract Electrons To Themselves (I.e., When.
Web compounds can be covalent or ionic. In covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs.




/some-examples-of-covalent-compounds-603981_final21-a3faebbe543e404fb951d2e789031f56.jpg)




